The Robotics & Automation Index (ROBO), the Artificial Intelligence Index (THNQ), and the Healthcare Technology & Innovation Index (HTEC) were not immune to the September selloff in equity markets and declined marginally in Q3. While investors debate the near-term growth and inflation outlook, businesses around the world are striving to accelerate their digitization and deploying automation at a record pace. In this report, we discuss key trends and big movers across our innovation portfolios.
Webinar Transcript:
Jeremie Capron:
Hello, everyone. And welcome to ROBO Global's October 2021 investor call. My name is Jeremie Capron. I'm the director of research and talking to you from New York City. And with me on the call today, two of our analysts from the research team, Nina Deka, and Zeno Mercer. So here is our agenda. We will review or three technology innovation portfolios, that is ROBO, HTEC, and THNQ. And we will be taking your questions, so please feel free to type them into the Q&A box at the bottom.
And before that, let me kick off with a brief summary of what we do here at ROBO Global. We are a research and investment advisory company that's focused on robotics, AI and healthcare technologies. And we are the creators of research-driven index portfolios that are designed to benefit from these mega trends. Today there's over four billion U.S. dollars in funds tracking with strategies, primarily in ETFs, on the New York Stock Exchange, as well as in Europe and in Asia.
And the most notable is ROBO, R-O-B-O, that was the first robotics, automation and AI ETF that started just about eight years ago in 2013. We also run THNQ, or THNQ, that is the artificial intelligence index. And HTEC, the Healthcare Technology & Innovation Index. Our strategies are based on a research-driven approach. And we combine that with the benefits of index investing and the ETF wrapper. So the portfolios are composed of best in class companies from around the world. We have small, mid, large caps. They are more or less equal weighted and they're rebalanced quarterly. So these portfolios have a very high active share. That means a low overlap with equity indices like the S&P500 or global equity indices.
And we started with ROBO, which covers the entire robotics and automation value chain, and the bubbles that you can see around it here, they represent the sub sectors of focus, and we'll be talking about that today. So we have key areas of application, like factory automation, like logistics and warehouses, like healthcare, food and agriculture, and so on. And also the enabling technologies that make robots and autonomous systems possible, like sensing, like computing. And in the past three years we started two additional index portfolios around areas that really stand out in terms of the potential for disruptive impact. THNQ on the left-hand side on artificial intelligence, and HTEC on healthcare technology and innovation on the right hand side. And they are designed using a similar recipe to ROBO in terms of the sub sector approach and the research-driven selection of best in class companies.
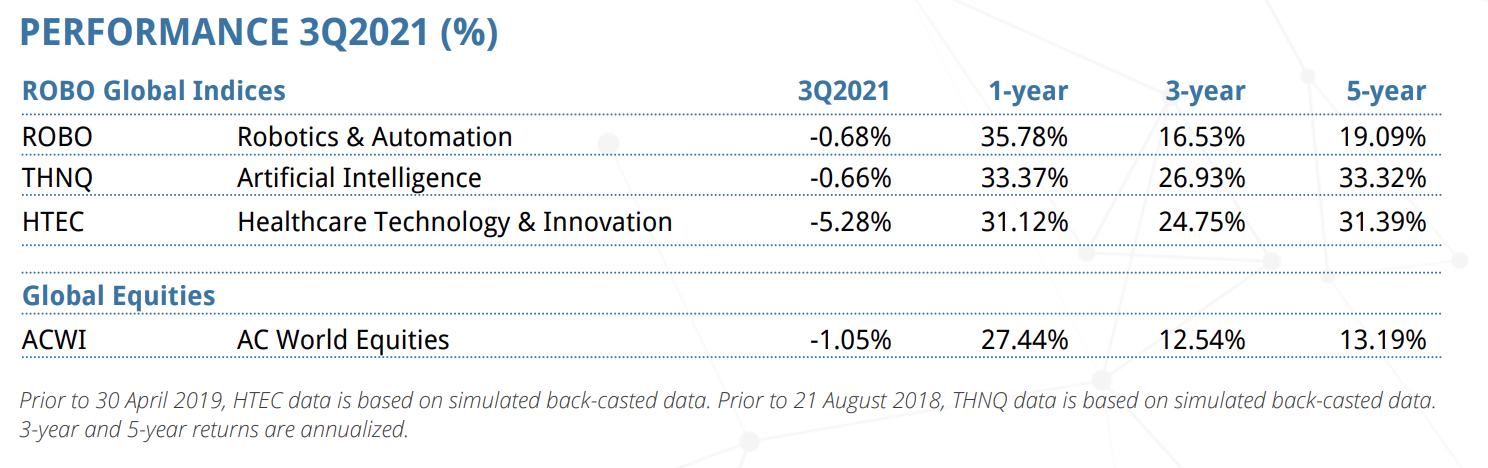
So let's talk about returns. This quarter, in the third quarter of 2021 global equities declined just over 1%, and we saw marginal gains in the U.S. that were offset by declines in emerging markets and a significant sell-off in China in particular. We had a very strong earning season early in the quarter and a run-up into August, but then growth and inflation concerns led to declines in September. If you look at the table here, you can see two of the three ROBO Global indices outperformed global equities, ROBO and HTEC declined a little bit, while THNQ was down, while HTEC was down more than 5%.
And you can see here that the three strategies have largely outperformed over the past one, three and five years. And please note that THNQ went live in August 2018. And so it only has a little more than three years of actual track record. And HTEC went live about two and a half years ago. So the data here includes a back desk for periods prior to inception. Whereas ROBO, these are all actual live returns for all periods because it's now turning eight.
Now, let me make a few comments on the market and our outlook. First, I'd like to say that our view that 2021 would be a boom year has largely played out and the global economic rebound continues to maintain significant momentum. We're not too worried about the recent downgrades to economic growth. The downgrades are largely due to the Delta variant wave that seems to have peaked by now, and also some supply-side bottlenecks. And if you take a step back, we're still looking at a much faster recovery than after prior global recession. And we see ample room for earnings to continue to grow both historical averages. And one important issue is rising inflation, and potentially a more meaningful tightening of monetary policy. And that is a fair concern because so far policymakers around the world have remained surprisingly supportive of massive fiscal and monetary stimulus.
And this is despite the evidence of rising prices and now more and more shortages. Think about semiconductors shortages. Think about shipping costs going through the roof. Think about energy. And also now labor shortages in the U.S. in particular. We think our portfolios would not be immune to a meaningful correction in the equity markets, especially if we see a monetary policy mistake of tightening too early, but we believe that they are very well positioned to capture the long-term growth and returns presented by the technology revolution.
And also the opportunities in the near term because the pandemic has clearly accelerated the adoption of these technologies. Last year we said that the digitalization of the economy had been turbocharged, well, this continues very strong in 2021. Businesses all around the world are striving to digitize, to automate, to increase efficiency and adapt to rapid changes in terms of what consumers expect. So if you look at the ROBO, HTEC and THNQ strategies, they are specifically focused on technology disruptors that are gaining share in this environment.
Many have been massive beneficiaries of this shift. Especially companies in the areas of AI, in factory automation, in logistics automation, in enterprise software, in healthcare technologies. And so it's probably fair to say that robotics, AI and healthcare tech are seeing a perfect storm of capital right now. A perfect storm of capital, that is the title of the recent report that our team published a couple of weeks ago. And you can find it and download it on our website.
On this slide you can see three quarters into 2021 we're looking at another record year for mergers and acquisitions, for venture funding. We have a record number of birth of unicorns. We have big IPOs, and in terms of M&A you can see here some of our index portfolio members that have received a takeout offer this year alone. So these are companies that are part of our portfolios receiving a takeout bid, and typically seeing a share price boost as a result.
Now, let's talk about ROBO, and then I'd pass it on to my colleagues to discuss HTEC and THNQ. ROBO is a research-driven index of the best in class robotics and automation companies from around the world. And on that next slide you can see that it has outperformed the World Equity Index over time, including in the past three years and five years, but it is a little behind so far in 2021. ROBO was down just under 1% in the fourth quarter, after rising 8% in the first half, and 44% last year. So we'll call that a consolidation in the past reports.
Now looking at returns by sector, you can see here on the pie chart on the left side, the 11 sub-sectors of focus for ROBO, and that is covering the entire value chain, from the core technologies that make automated systems possible, like computing and sensing, and applications across manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, food and ag, et cetera.
And during the quarter we saw seven of the 11 sectors with gains, and the best performing sectors were at the top of the tables here on the right hand side business process, automation and integration and computing and AI. So what is business process automation? It's about automating and integrating the business functions, it's primarily software. So you'll find companies like ServiceNow that focuses on IT and enterprise workflows. You'll find companies like PTC and Decile Systems over in Europe or Autodesk. And they focus on design functions and virtualization, things like the digital twin of real world assets. And you also find Blue Prism, which makes software robots. And that was one of the best performing stocks in the quarter after agreeing a $1.5 billion offer to go private. So we saw copying the stock towards the end of the other quarter.
Factory automation stocks. I want to touch on that because they were presented around 40% of the index by weight. They were mixed in the quarter. They tend to be more cyclical and sensitive to changes in the economic outlook. But we believe that the cyclical recovery in factory automation is really in full swing by now. We've entered the fifth quarter of improvements. And historically the upswings have been a series of 10 to 14 quarters on average. So we think factory automation earnings will continue to go up and they will probably reach a new high in 2022 next year. Now, in terms of the under-performers, you can see at the bottom of the table here that 3D printing had a pretty rough quarter. It was down more than 22%. But you can see next to that 22% number here that over the past 12 month the sector is still up almost a 100%.
And so that pullback that we saw in the quarter was driven by 3D Systems. So if we move to the next slide, I want to touch on 3D Systems. That's a provider of 3D content to print solutions, so 3D printers, but also the services around it and the software around that. They have very strong positions in 3D printing for medical applications. So think about implants and dental and things like that. And they're also very strong in industrial applications. And they are a member of both the ROBO index and the HTEC index. Now the stock was down after an extremely strong 280% plus gain in the first half of the year. These companies have made very significant progress in terms of its restructuring plan that they announced in the summer of last year. It's showing an acceleration in the top line growth, it's showing expanding margins.
And most recently they spend $180 million to acquire a company called Oqton that has a cloud-based platform for manufacturing operating systems. So you can see 3D Systems is also moving aggressively towards a software business model. Now, let's talk about some of the top performance during the quarter. And the first one is Ambarella. That was up 46%. And Ambarella is a leader in video processing semiconductors, and it had its first big hits in drone cameras and video surveillance. But what we like about Ambarella is that it's rapidly turning into an AI company. They have computer vision capabilities that are gaining significant traction with major players in video security. So these guys use Ambarella's technology for facial recognition, for behavior analytics. They do things like intrusion detection and so on. And also in automotive where the computer vision technology is used for advanced driver assistance and autonomous driving.
And Ambarella reported very strong margins in the quarter that's really supporting our view that they remain very competitive against their bigger peers like Intel and Mobileye. And we think Ambarella is a highly attractive acquisition target. The next one I want to touch on is HollySys. This is a Chinese provider of automation control systems. They're a leader among the domestic Chinese players, and they also receive the new offer to go private, $23 per share. So that will present about a 1.4 billion U.S. dollars. And at the end of last year HollySys had already received a low-ball offer at $15 a share from the consortium that was formed by a former CEO of the company. This time this higher offer at $24 coming from the consortium, including the founder of the company who retired, I think about six or seven years ago.
And this offers also attracted senior leaders of the business. Current leader, the CEOs of the companies are supporting it. So we think HollySys is very likely now to go private. Now, let's touch on two new companies that were included in ROBO at the September rebalance. The first one is AppHarvest, which comes into a food and agricultural automation sector. It went public in February. It raised just under half a billion dollars in a merger with no risk capital. And what AppHarvest does is that they build and they operate greenhouses that are highly automated, very water efficient. And their goal is to grow fruits and vegetables using a very local supply chain, and a lot of automation and AI. They have plans to run five facilities by the end of the year. And they will have 12 farms by 2025. They are going to be growing mostly tomatoes and leafy greens.
So this company is based in Kentucky. All right, the next one is GXO Logistics. That's also in a newly public company. It's what formally was the logistics division of XPO. So GXO is a global leader in what we call contract logistics. They provide highly automated supply chain management solutions for very large companies, multinational blue chip companies like Nestle, like Nike, those companies that choose to outsource their logistics to specialists that can leverage the power of automation. So it's the handling, it's the storage, the distribution of warehouse-based goods. And if you look at GXO, they have a very high exposure to e-commerce of course, e-commerce and omnichannel retail, that's more than 50% of their revenue. So I'm going to stop here and pass it on to Nina to talk about healthcare technology. And before I do that, just want to remind everyone, you can ask your questions using the Q&A box at the bottom. On to you, Nina.
Nina Deka:
Thanks, Jeremie. All right, so now we're going to transition over to HTEC. This is the ROBO Global Healthcare Technology & Innovation Index. And so, first of all we'll talk about the performance. Healthcare innovation, as we're sometimes seeing this quarter is a marathon, not a sprint. And here we have during the quarter the index returned a loss of 5% and that underperformed the global equity index of negative 1% and then the global healthcare index, which was 1% returns over the quarter. But if we look at a three-year trajectory healthcare innovation, we still have very high conviction that there are still a lot to gain over time, or over the long run. The three-year returns you can see for the HTEC index are roughly double the performance of the standard global healthcare indices. And so people often ask, "Well, what's the difference between HTEC and some other healthcare indexes?"
And so I just wanted to show you in the next slide, when you look at the sub sector breakdown, we focus on a very diversified list of sub sectors. We've got nine different sub sectors here that we focus on. And these are the areas in healthcare that we believe represent the most disruption over the next decade. The companies that are market leaders, technology leaders in these areas, such as medical instruments, diagnostics, genomics, telehealth. We believe that over the long run there is a lot of disruption that we're going to be seeing, and we're only just in the beginning. If you look at the right side of this slide, we show the sub-sector returns. And as you can see, let's start with sort of the needs improvement category. The telehealth, it returned negative 30% during Q3. This sub sector was pressured largely by some of the companies in the index that are China-based, Alibaba Health, JD Health, for example, Ping An Healthcare.
These are market leaders in China for telehealth. They distribute pharmaceuticals to consumers, and they have a lot of upward trajectory for growth as more and more drug and pharmaceutical purchases move from the mom and pop pharmacies and the brick and mortar pharmacies to online purchasing. Also, we're in very early days with these companies, but we expect to see a high degree of M&A in the future where these companies look to expand their healthcare services capabilities. For example, go further into telemedicine services, like doctor patient visits, as well as providing digital health platforms to hospital systems in China. So, we expect to see a lot of growth in this sub sector over time. And these are just very early days. Teladoc is another global market leader in this space. Teladoc reported earnings last quarter, where they indicated that their telemedicine visits were up 28% year to year. To us, that is an indicator that telemedicine is here to stay, and that there's still so much more growth to come.
And remember, year over year growth in telemedicine is pretty significant, because second quarter last year was the height of the pandemic when no one could see a doctor in-person. So, for the company to grow a 28% over last year with a high volume is just a strong indicator that we're only just the beginning here. And we expect to see a lot more when it comes to hospital integrations and doctor to doctor communication, device to doctor, device to patient, there's still so much more integration that's going to be coming tele-health. So stay tuned there. And then maybe we'll transition to one of the out performers, process automation. Process automation sub sector includes a bunch of companies like Catalent as shown here on this slide. T Can is another one Thermo Fisher Scientific. When we think of process automation in healthcare, we think about the companies that are enabling other healthcare innovators to do what they do best. For example, an estimated one-third or 37% of all drugs that are manufactured are actually outsourced to other companies, known as contract development manufacturing organizations.
And an estimated two thirds of all clinical trials are also outsourced to companies like IQVIA for example. And so here we'll dig a little bit deeper into Catalent. This is a company that returned the most in the process automation sub sector. Catalent is less known by many people, but they were actually one of the partners of both Moderna and J&J for manufacturing their COVID vaccines. This company has been around for a long time. In fact, they invented the soft gel. Many people are familiar with taking soft gels versus the powder-based oral drugs. So Catalent is a company that really has focused in the last five, 10 years on investing its capabilities in biotech. So what this means is that we know that there's been a lot of biotech investing activity. A lot of IPOs, a lot of startups, a lot of companies that are creating one drug or a couple of drugs, and these drugs are focused as we get more and more precise with medicine in very individualized therapeutics.
So one drug might only aim to treat 20 people during a clinical trial, maybe five people. It's really difficult to manufacture a drug at scale when there's not that many people that are going to wind up taking it. So a lot of these biotech startups don't have the bandwidth to manufacture the drugs for their clinical trials, or even after the drug gets FDA approved. So they outsource it. And Catalent has gone all in, on being able to make a small quantity of these highly specialized drugs. And this mRNA therapy is a case in point. They invested in the ability to manufacture mRNA. And now they've got a dedicated manufacturing line that is enabling them to become a subject matter expert. So think about the longterm. We now have mRNA as a new therapeutic, introduced to us through COVID-19. But over time there's going to be many more mRNA therapies that are going to come to market.
Catalent is very well positioned to capture that growth over a fast-growing theme. And that's just one example. And so we'll just move on quickly to the other leaders of the index over the quarter. Moderna, as I mentioned, returned 64%, no surprise there, a lot of growth around the world providing the COVID vaccines. But really what we're really excited about here with this company is now that mRNA is a recognized therapy, we expect to see many more therapies coming through, and Moderna has a very rich pipeline. Their progressing trials for a virus called CMV for flu. They over time expect to launch a flu combined with the COVID vaccine potential, and so some really exciting things to happen there well beyond the pandemic.
And then with Dexcom. Dexcom is reported strong growth year over year in revenue over the quarter, they also have filed for their CE mark approval. This is the FDA approval in process in Europe. They filed for their next generation continuous glucose monitoring device. This is a diabetes company. And so they expect to launch that in Europe by the end of the year. This new generation CGM device that they're launching is the size of a nickel. It's like 60% smaller than what's currently available and widely used on the market. So Dexcom is known for making the most accurate CGM device on the market. And we're really excited to see a large growth trajectory there as Dexcom further looks to have more people using the CGM device, like people with type two diabetes.
And then we'll just quickly show you the new additions to the index in the quarter. A couple of interesting companies here, Akoya is really focused heavily on spatial biology. So this is bringing some neat exposure to spatial biology into the index. This is a technology that many people have heard of next gen sequencing in genomics, which is just a way to sequence the DNA. Spatial biology is considered the next gen sequencing in that there's a huge trajectory for adoption. And what it means is that it basically gives you more detailed view of a human genome. So if you were to compare this to say, let's say you wanted to make a smoothie and you blend all fruits together, and then you don't really know, you think that there's raspberries in there. And then there's probably some strawberries and maybe some banana, but you're not sure how many of each and what the portions and ratios are. But then if you take that analogy and look at say a fruit salad, then you can count how many fruits, pieces there are of everything in there and where they're located in the bowl.
That analogy kind of gives you an example of how you can really look at say a tissue sample and know exactly where the DNA is that's causing the different types of cancer and where there might be variance and different mutations that might also be causing cancer. So really exciting stuff there. And we've got, I could go on for ages on these other companies and the cool technology happening there. Twist is giving, it's a great enabler of synthetic biology. Fate, we can talk more about that in the Q&A as well. So with that I'll stop and pass it along to our colleague to talk about THNQ. Zeno, I think you're on mute.
Zeno Mercer:
Thank you, Nina. All right. Hey everybody, I'm Zeno. I'm going to cover THNQ today, that's T-H-N-Q. So THNQ is a pure play artificial intelligence strategy, aiming to capture both infrastructure and applied innovation in the space. Since the index launched in late 2018, we've seen the index double in value as adoption of these technologies grow. Of course, over the past year we saw the rapid digitalization of nearly everything in our lives. And as such we're really excited about this space as the AI market is projected to generate over $400 billion in revenue by 2025, up from 70 billion in 2020. So performance over the past year, we had a 67% gain in 2020. The THNQ index was up 7.4% year to date at the end of the third quarter, slightly outperforming global equities for a 0.7% loss for the quarter. This year alone the THNQ index has had seven takeout offers from a mix of strategic and financial sponsors.
Now moving on to our sub sectors. So six of our 11 sub sectors posted positive returns with highlights across network and security, consulting services and business processes. Those were leading the way while cloud providers, healthcare and big data and analytics under performed. Now, it seems like everyone in the world is focused on, and for good reason, the importance of semiconductors and supply chain issues that continue to be reflected in auto electronics, nearly everything now, as demand skyrockets. And previous cycles is higher demand led to overproduction and subsequent oversupply and reduced prices. This time we believe that we have way more secular trends going for the sector, increased cloud computing, wearables, mobile, and 5G. Enterprise AI, autonomous vehicles, IoT remote work, need I go on? And of course, blockchain, all creating demand up and down the value chain.
Network and security, moving on to the next slide outperformed for the second consecutive quarter up 10%, and up 65% over the past 12 months. On the more security side, you might have seen things in the news recently about AI and security. We have Palo Alto Networks and Rapid set in leading the way up 29% in 19% respectively. They were both providers of advanced cybersecurity solutions. And we were seeing multiple secular trends in the cyber security market, which is expected to double over the next five years with spend expected to grow more than $200 billion. This is due to increased cyber secure attacks or sophisticated attacks and higher stakes. We have now healthcare, finance, commerce, government and infrastructure and more, all basically on the cloud now, which is it's merits and improvements. But this has also introduced a plethora of vulnerabilities, which only boosts demands for the services.
On the more network side, you have companies like Pure Storage, which were up 29% for the quarter, which continues to see high deployment of their industry leading scalable cloud storage solutions, providing more autonomus and faster deployment for customers who continue to see increased span around AI and cloud architecture. Of note, Pure Storage recently launched an industry first solution that allows autonomous storage as a code for on-demand storage solution, which can massively speed up deployment times. So this should make it even easier and secure to spend money on their services too.
Moving on to the next slide and next sector, we have cloud providers, which underperformed and we're down 9% for the quarter. Overall mix results as leading Chinese AI companies, such as Alibaba and Tencent valuations faltered as the overall Chinese market dropped under pressure from both political and regulatory risk, leading to multi-year low valuations. Baidu, another index member, one of the world's largest AI companies at the forefront of numerous innovations across autonomous vehicles, advertising, search and more, was trading at just 1.5 equity value of the sales. We expect a recovery here and so far in Q4 where things have been mostly flat or down worldwide, these Chinese AI companies are up 10 to 15%. On the more positive front Cloudflare was up 6.5%. Now, for those who don't know, Cloudflare provides network services and security solutions for website hosting and content delivery, also IoT and cloud platforms, and it is up 40% so far in Q4.
As revenue is expected to go 48% year over year as they see a massive demand for their services. They continue to innovate. And as example, one of the recent products they released is to prevent phishing attacks using machine learning. So moving on to the next slide, thank you. One of our top performing companies I wanted to highlight is Atlassian. So Atlassian gained 52% over the third quarter. They are a Australian-based cloud technology solutions provider focused on workflow and AI collaboration tools for developers and enterprises with over 200,000 clients now. Atlassian has delivered consistent 30% top-line growth in the past few years, driven by its breadth of technology and marketplace in the cloud market. This also includes devops and this helps empower the teams and digital technologies for the world-leading applications. And so they're seeing strong adoption by large and small enterprises alike.
Next I'd like to circle back to Palo Alto Networks, another strong performer for the quarter, which is up 29%. So Palo Alto Networks is the global cybersecurity leader with both hardware and software solutions, utilizing proprietary cybersecurity artificial intelligence, and they hold the largest market share among its peers with tens of thousands of organizations. And they are a leader in Gartner's Magic Quadrant for these solutions. Subscription revenue continues to grow strongly, and before COVID we were at 36%, there's now 44% of the revenue. So that's very sticky business and consistent revenue streams. Another highlight and growth driver is earlier this year they received FedRAMP certification for several of their cloud solutions. This is essentially the seal of approval for technology and security for the U.S. government. So we're going to start seeing more and more deployment across federal and municipal government agencies.
Lastly, I'd like to cover a new member spotlight. After four new additions last quarter, we just had one this quarter in our business process sub sector. Upstart Holdings is an AI-empowered lending platform that disrupts the traditional lending process by essentially creating their own credit scoring system. And this helps automate lending. So they also help with both the lending and borrowing platform for both sides. So what they're doing is providing personal loans to a massively underserved unsecured market in auto credit and mortgage markets. Upstart is gaining market share and is projected to grow top-line revenue 220% to reach over a 100 billion in revenue next year, as they continue to gain partners in diversified revenue streams in this space. As an example, this past week they partnered with Kentucky's largest credit union to help power their back end. One last thing I wanted to cover is Aspen Tech. Jeremy mentioned we've had lots of takeouts. We've had seven so far this year, including Aspen Tech, which saw a $11 billion takeout by Emerson Electronics this past week. Now I will pass it back to Jeremie who will help wrap things up.
Jeremie Capron:
Thank you, Zeno, thank you, Nina. We're going to move on to the Q&A section of this call. And I see we have a few questions that have already come in. Please feel free to add yours. And we'll take the first one. Do ETF capture robotics and AI in the ag sector? Yes. Short answer is yes. If we can go back to this slide that shows the ROBO sub sectors, you can see the food and ag sub sector in there. We think there's a lot of very exciting development around ag technology and food and beverage manufacturing, and that the intensity of automation in this sector is growing very rapidly. And so today the food and ag sector is just around 5% of the index, so it's one of the smaller application sectors. The bulk of the activity today is still in manufacturing and logistics.
And then they're really up and coming sectors of adoption are healthcare and in food and ag. So in food and ag, what you're going to find is companies like, companies that automate the production lines for food and beverage. So the GEA Group in Germany that's focused on the dairy industry, and they do things like cow milking robots as well. You'll find companies like Krones, also in Germany. Krones is the world leader in bottling machinery. And you'll find companies like John Bean that's focused on the protein market. So automation equipment for the meat industry. And then, companies like UpHarvest that I touched on early on the call. That's a company that's a recent addition to ROBO and that's highly automated greenhouses. And then, in the private side earlier stage companies we're seeing very exciting developments. Companies that are using facial recognition type of computer vision to analyze each and every plant by rolling over the crops, using a tractor and behind it driving computer vision equipment.
And you're able to analyze the levels of hydration, the potential contamination by diseases, the need for pesticides. And the results are quite fascinating. We're able to reduce the use of pesticides by a factor of 10. So some very exciting developments there. Also, on the private side we expect a lot of these companies will eventually go public like UpHarvest did earlier this year.
And then we'll move on to the next question. I want my colleagues to jump in here. Let's talk about small and mid cap innovative companies. How do you go about discovering them? And particularly the ones that go unnoticed by the sell side. Zeno, do you want to go in first?
Zeno Mercer:
Yeah, I can start here. So essentially the way we go about this is, we really take a holistic look at the spaces we're looking at, our sub-sectors. While we do obviously have access to and use lots of resource sources, we do come up with our own kind of top down bottoms up approaches to looking at different problems and opportunities in society. So, looking at smaller, you mentioned, not really covered. I mean, while that is important, while factors like liquidity and access and market is important, we're looking at finding the best in class technologies and we have our own proprietary scoring system. We really take a deep look at the teams, the innovation factor behind these technologies and what they can do, and how that adoption will play out, how they will capture revenue in the business model. So yeah, I would say that basically summarizes my approach and our approach on the AI side.
Nina Deka:
And then in terms of healthcare, it's actually quite similar across the board, across our indices. But there, if you look at the private world, there's been just an enormous amount of investment in healthcare innovation from an early stage to late stage venture habitual standpoint. And we have seen an influx of new IPOs, particularly in the healthcare IT space in what we call data analytics or telehealth in our portfolio. But, and then we're also seeing a lot of investments via M&A. So the way that we do this is we look at, I guess, a top-down approach. We look across the different industries of healthcare. I mentioned earlier there are nine sub sectors, but within them there's also, like for example, you look at medical instruments. Within medical instruments there's going to be focus on cardiology, diabetes, 3D printing.
There's a lot of different places, same within robotics. There's going to be focus on surgical robotics. There's also robotics used in the pharmacy. So we look at the different applications across our nine sub sectors and of different indications and areas of healthcare. And then through there, through deep fundamental research and industry analysis, that's where we uncover who the players are. A lot of them are private. A lot of them are small, mid cap and many are large cap. And then what we also see through M&A is that a lot of the companies wind up getting acquired, often by companies that are already in our portfolio. So it's, I think it's just a broader market level top-down approach that helps us capture the different size companies that we then evaluate with our proprietary scoring system to determine whether or not that they'd be a good fit into our index. Hope that answers your question?
Jeremie Capron:
Thank you, Nina. So let's move on to the next one. And actually there's a couple of questions around the growth orientation of our portfolios, and whether they would perform as well in a value market. I think that's a very fair question. And certainly on the healthcare tech side and on the AI side, those are definitely high growth portfolios. And so if we're in a value market, you wouldn't expect those portfolios to perform as well. That is a fair comment. I would just highlight that on the ROBO side however, there's a lot of value in the portfolio. In fact, was just looking at my screen a few minutes ago, and we have more than 20 companies in the ROBO index out of just over 80 total members that have a forward P/E under 17.
So significantly below the market average. And typically those companies are more cyclical in nature. They are involved in the factory automation world. There tend to be more capital goods types of businesses selling equipment and machinery. A lot of these stocks are in Japan, and right now they are cheap. And typically what you see when we have a rotation into cyclicals and the value areas of the market, we see those stocks perform very well. And if you go back to the long-term performance chart of ROBO, you will see that it performs well, even in a value type market. And I would highlight in particular the first quarter, and we had the sell-off, the COVID lockdown driven sell-off in March of 2020. In Q1 of 2020 ROBO outperformed global equities.
And then we have a question around valuations, if we could comment on valuations for each index? And I'll start with ROBO and pass it on to Zeno and Nina for HTEC and THNQ. So in terms of valuations for ROBO, today the index is trading on a forward P/E of 29 times. And that is a 20% premium to the long-term average, which is just around 25. So we are trading at a premium, but it's also very clear that the earnings trajectory is very remarkable right now. In the second quarter we saw EPS beat by 12% at the median, and EPS growth in the second quarter was 68% year over year. That was the strongest growth since the inception of the index in 2013.
Now, the hurdle was low. A year ago in Q2 you had a 19% year over year decline, but that means we're already making new highs in terms of earnings overall in aggregate for the fund. And we expect EPS to grow by more than 80% in the third quarter, and for the full year 40% in 2021. So we are we on a faster growth trajectory, and that typically deserves a higher forward P/E. So Nina and Zeno, can you please comment on valuations for THNQ and HTEC?
Nina Deka:
Yeah, definitely. So for HTEC we typically look at, because so many of the companies are not yet profitable, they're in a high growth state. So we look at forward EV to sales as a good benchmark for valuation. And during the quarter, as I mentioned, the index returned negative 5%. So the evaluation is actually low now relative. It's at 6.4 times for EV sales. That compares to about 6.95 times year over year. So this quarter last year it was just about seven times EV to sales. And last quarter it was, so it's also down sequentially. Last quarter it was 7.1 EV to sales ratio. So some would argue that this could appear to be a nice entry point for HTEC.
Zeno Mercer:
And for THNQ, kind of similar to what Nina said. We've seen some valuation contraction, especially as we mentioned earlier among Chinese companies. So right now we've got forward EV sales of 9.38. Obviously we have a lot of high growth tech companies that have gained a lot of steam during and because of the pandemic. We've seen adoption that probably would have taken five to 10 years, and some of these companies have a mix of both sticky businesses and lend and expand opportunities. So, similarly think that from a valuation perspective and opportunity perspective that earnings are going to continue to grow. We're going to see more profitability, margins will stay strong, and yeah, just pretty positive outlook here for that sector.
Jeremie Capron:
Thank you both. Let's move on. I see we have some questions related to specific companies, so maybe we can take those. We have one on Fate, that's a new member in HTEC. We have one on Butterfly Networks, maybe Zeno, you can start on Butterfly Networks, and then Nina, can you take Fate?
Nina Deka:
Sure.
Zeno Mercer:
Sure. So Butterfly Network for those who are not familiar, is a best in class portable ultrasound device with an AI company attached to it. Just a little bit about the market in the world. You've got about two third of the world that doesn't have access to reliable diagnostic technology. And this is a mix of cost, because these devices traditionally cost more, infrastructure and having local experts and people able to actually handle and know what they're doing in these areas. So you have so many preventable health outcomes that can be solved through ultrasound intervention and diagnostic discovery. So, Butterfly Network can, and the goal is to essentially provide wayman, anybody with the ability to use this combination of their really proprietary great ultrasound with AI and remote access telehealth for second opinions and live of guidance. And they continue to add new capabilities, and this is accessible through a subscription service.
So you have both a hardware and software play. And just, kind of otherwise you've got, the average ultrasound technician, over $85,000 a year in the U.S. Other places in the world can't really afford that. And a platform like this could allow massive health opportunities and improvements to quality of life. So you've got general medicine, emergency medicine, anesthesiology, hospital. They've added vets. So, all the vets around the world, with horses, doctors, cats, dogs. And in terms of growth opportunities beyond that, they're even looking at beyond improving their core ultrasound going into wearables, which while they haven't announced anything specific, given the innovation behind their Butterfly IQ device, we expect nothing less than something pretty innovative there.
Nina Deka:
And I can take over with Fate. So Fate Therapeutics is a company that's focused on something called NK cell therapy, NK stands for natural killer. This is really exciting stuff here. So I guess if you were to compare NK to CAR T therapy, maybe many people have heard of CAR T therapy. CAR T is something that has been able to essentially cure cancer, but it's got some limitations. In order to treat somebody for using a CAR T therapy you need to take a sample out of the patient, ship it off, have the actual drug manufactured, using the cells that came from the patient, ship it back, and then administer it. And it could be, it has side effects. It could be actually toxic inside the human body. And it's very expensive. That entire process costs a couple 100,000 dollars.
With Fate, with natural killer therapeutics, they're actually extracting stem cells that they can use and create virtually anything they want with. And so what they're using stem cells for is to make something called natural killer, and they can replicate and make many of these. And it's basically off the shelf and they can store it. And then you can, once you manufacture the NK cell, you can then use it on anyone. So you don't have to then take the patient's specimen, ship it off, and then administer it. You can just literally order it and administer the treatment on the fly, and it's already ready to go.
NK cells are also known to be less toxic, have a less toxic response when administered into the human body. And it also costs a lot less to administer their therapy. It costs about $2,000 versus a couple of 100,000 of the CAR T. So these are still in clinical trials, but they are advancing. And so we are awaiting more data that supports that when this therapy is administered, that it lasts as long as CAR T. So real exciting stuff here in NK, and I hope that we'll have more to report in the coming years.
Jeremie Capron:
So I hope that answers your questions. If you have more questions, feel free to direct them to our website or info@roboglobal.com. I want to reiterate that we do share some of our research via a biweekly newsletter that you can sign up for on the website, roboglobal.com. And we very much look forward to speaking to you again very soon. Thank you all, and have a great day.